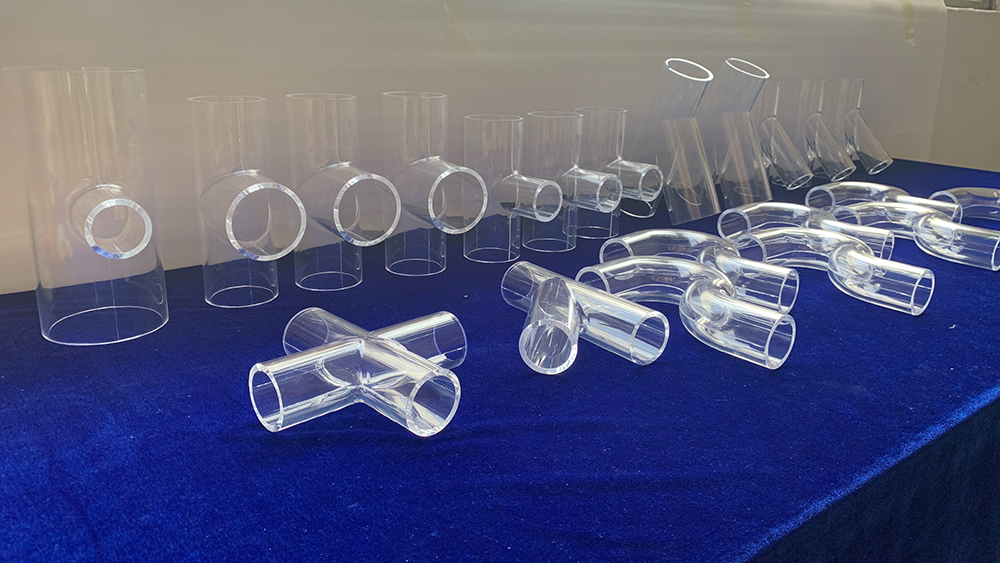
A prototype model—often referred to as a rapid prototype—is made after a new product’s design is completed but before formal production and tooling begin. Based on the product’s design or engineering drawings, one or more physical models are created so we can visually and tangibly evaluate what the final product will look like. This allows us to verify whether the appearance aligns with the design intent, whether the structure is reasonable, how the product might perform in the market, and whether it can pass various environmental tests.
As competition intensifies across industries, the speed of product development has become a key factor for success. Rapid prototyping significantly accelerates the development process, enabling companies to iterate faster and reduce risk. For this reason, the prototyping industry has emerged as an independent, fast-growing field.
Why Prototyping Is Essential
A. Validate the Product’s Appearance
A prototype is not only visible—it is something you can physically touch. It provides designers with an intuitive, real-world representation of their ideas, helping avoid the common pitfall of “looks good on paper, but not in reality.” Therefore, prototyping is indispensable during new product development, especially for refining shapes, forms, and visual details.
B. Validate the Structural Design
Because prototypes can be fully assembled, they reveal whether the internal structure is reasonable and how easy or difficult the assembly process will be. This allows teams to identify issues early and resolve them before committing to tooling.
C. Reduce the Risk of Opening a Mold Too Early
Tooling is expensive—large molds can cost anywhere from tens of thousands to millions. If structural or design issues are discovered after the mold is made, the losses can be substantial. Creating a prototype first and confirming its correctness greatly reduces tooling risk and prevents costly rework.
D. Accelerate Time-to-Market
Prototyping enables you to promote the product, conduct early-stage marketing, and prepare for production even before the mold is completed. This early engagement helps brands capture market opportunities faster.
E. Support Small-Batch Production and Trial Sales
Prototypes can also be used for low-volume production and assembly during trial sales. Feedback gathered during this stage can be quickly applied to improve the design before finalizing the product, significantly lowering market risk.


